Cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells divide uncontrollably and can invade nearby tissues, forming a mass or a lump called a tumor. It can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer, which affects 1 in 5 people. It's often a result of excess sun exposure over a prolonged time and shows varying symptoms based on the type of skin cancer. These may include discolored patches, bumps, or lesions that vary in shape and size. If caught early, most skin cancers can be treatable. Treatment options include Mohs surgery, cryotherapy, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
To know more about skin cancer types, stages, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, read this informative blog. Knowing the signs and symptoms will help you seek medical help immediately.
Skin cancer is a disease that involves the growth of abnormal cells in the skin tissues. Normally, as the old skin cells age and die, new skin cells are formed to replace them. When this cycle does not go as it should due to a variety of factors, like excess sun exposure, cancer develops. Skin cancer may be benign or malignant.
There are three main types of skin cancer, namely:
Other cancers:
Kaposi sarcoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
Sebaceous glands carcinoma
The main cause of skin cancer is increased exposure to sunlight. Excess UV light damages the DNA in your skin tissues, causing the growth and multiplication of abnormal cells. These cells rapidly divide in a disorganized manner, forming a mass of cancer cells.
Anyone can get cancer irrespective of age, sex or race. However, certain risk factors may increase susceptibility. These include:
Skin cancer symptoms include:
Depending on the type of skin cancer, it looks different. Remember to check for the ABCDE rule:
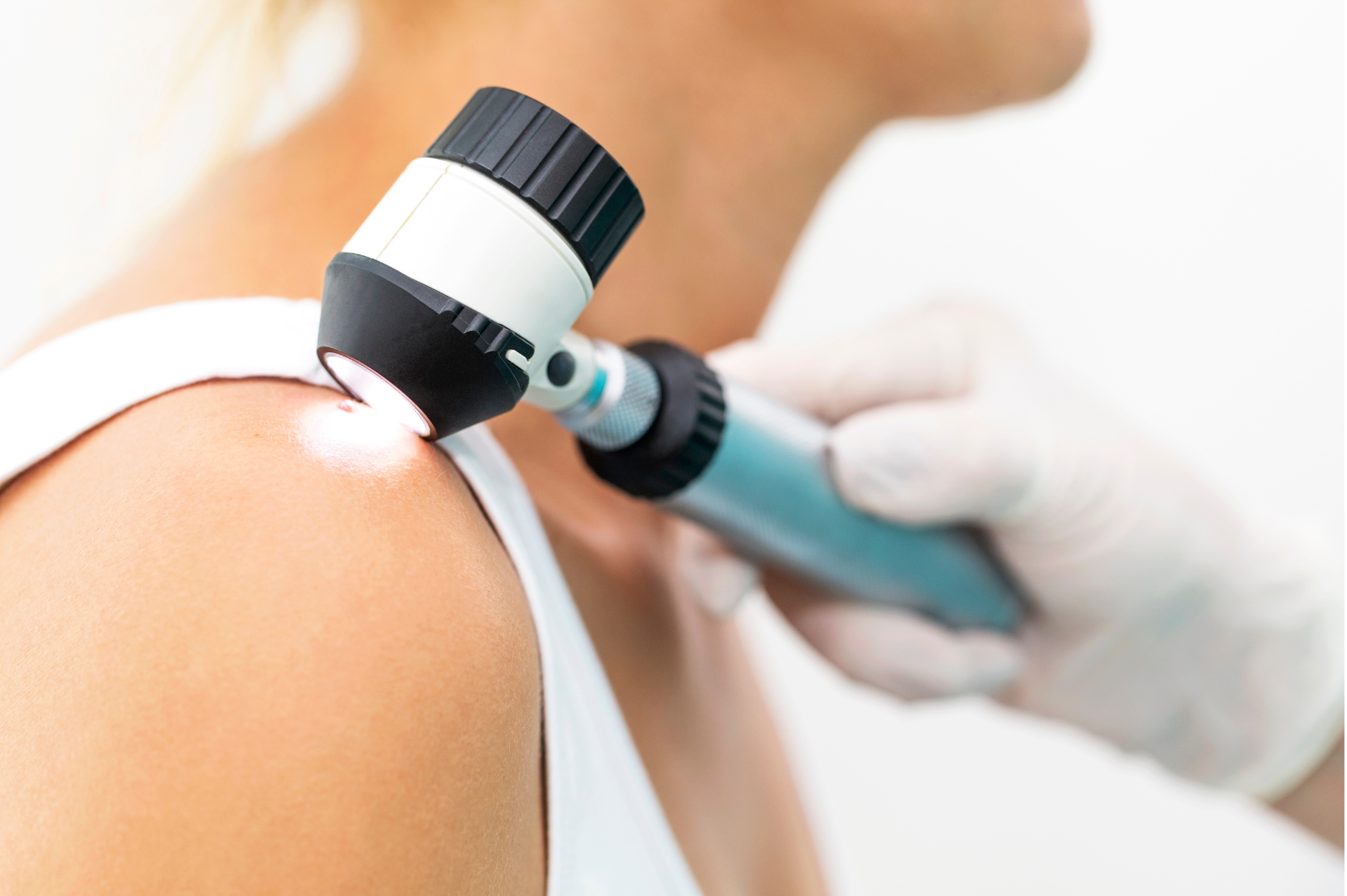
Your dermatologist will evaluate your symptoms of mole changes or new mole development. Later, they will examine your skin all over your body, especially your face, nose, scalp, back, genitals, and buttocks. If your doctor suspects skin cancer, they may perform a biopsy.
There are different stages for melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers.
Stage 0: Melanoma is present only in the outer skin layers.
Stage 1: There is no evidence of spread, and it is highly curable
Stage 2: The cancer may likely recur, but there is no evidence of spread
Stage 3: The melanoma has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 4: The melanoma has spread to the distant lymph nodes or distant internal organs
Stage 0: Cancer is only in the top layer of your skin
Stage 1: Cancer is in the top and middle layers of the skin
Stage 2: Cancer is in the top and middle layers of your skin and may target your nerves and deeper layers of skin
Stage 3: Cancer has spread beyond your skin to your lymph nodes
Stage 4: Cancer has spread to other parts of the body and internal organs
Common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Ways to prevent skin cancer include:
Skin cancer is a common type of cancer that can affect anyone. However, excess sun exposure is a prime factor that may cause abnormal cells to multiply and divide disorganized. Check for early signs of skin cancer and seek medical help right away since skin cancer at the early stage is the most treatable and curable. Take necessary preventive steps to protect your skin from the sun. Also, schedule regular skin exams with your dermatologist.