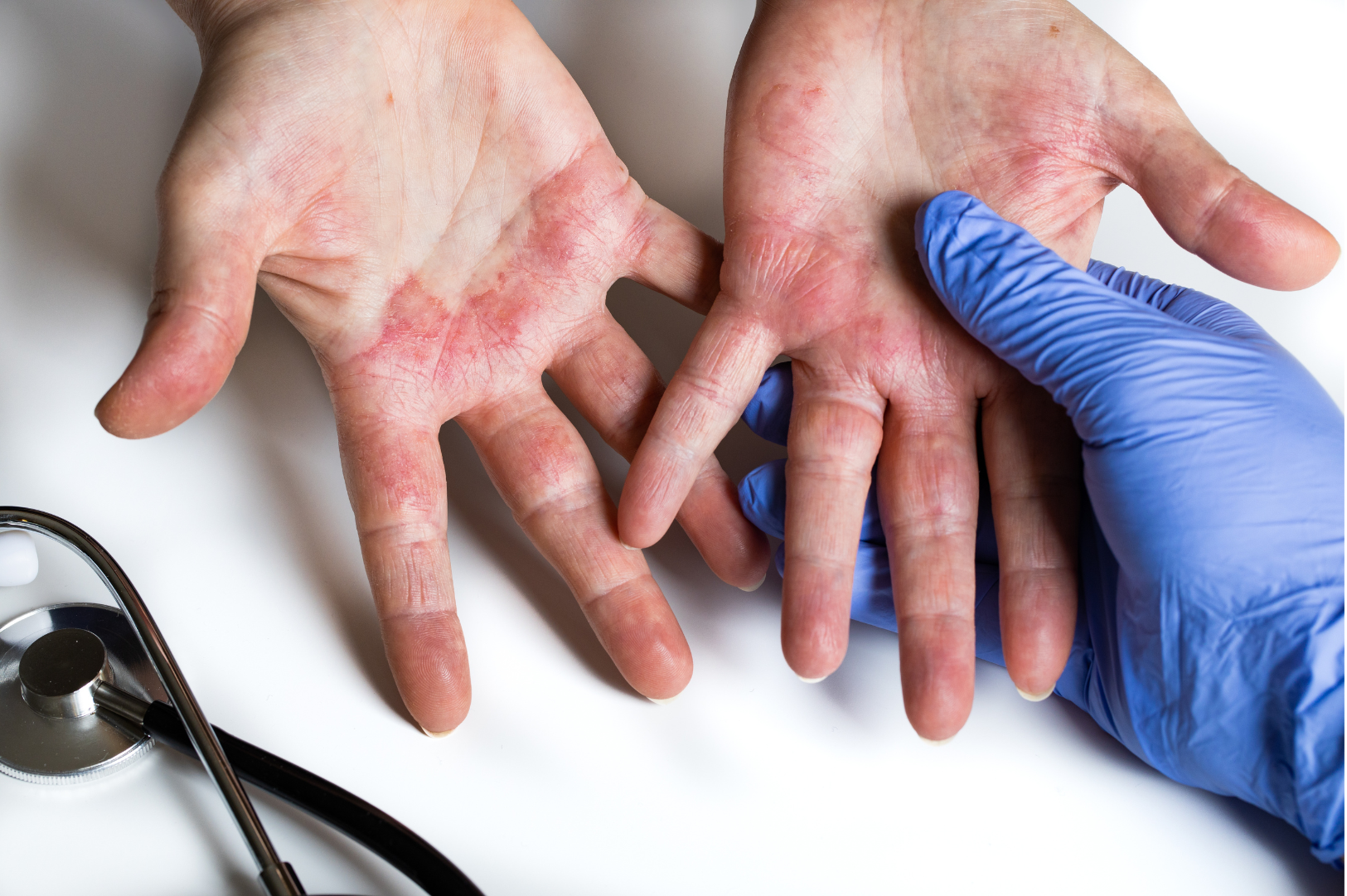
Skin conditions are common and may always manifest as a skin rash. This could be in the form of red, inflamed discolouration or flat lesions. There could be several reasons for the development of an abnormal skin rash. It could be due to an allergy, bacteria, fungus, or a virus. Skin rashes developing due to allergic reactions to any substance or environmental pollutant is known as "Contact Dermatitis"'. The skin rash may be flat, with red patches or discolouration that can swell, be itchy, and be uncomfortable. Knowing what causes an allergic reaction can help prevent skin inflammation or halt its progression.
Let's dive into what contact dermatitis is, its types, what causes it, how it looks, its diagnosis, and treatment options.
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that develops as a reaction to a chemical or other substance. This is usually not serious or life-threatening but can be extremely uncomfortable due to the constant inflammation and itching around the affected skin. The term dermatitis means some sort of skin irritation or inflammation. You may develop contact dermatitis by coming in contact with a substance, organism, object, or chemical irritating your skin.
Contact dermatitis can affect anyone, irrespective of age and gender. However, certain people and professions are at a high risk of developing this skin condition. These include:
There are two types of contact dermatitis, namely:
Any physical contact with an allergen or an irritant causes contact dermatitis. If your body doesn't like something you touch, your immune system begins to react. Your white blood cells begin to respond to the allergen or irritant, which can cause an itchy rash. The rash may appear in minutes if caused by an irritant or may take hours or days to appear after an allergen exposure.
The symptoms of contact dermatitis include a skin rash that is:
The skin rash due to contact dermatitis may appear anywhere in your body that comes in contact with the allergen or irritant. However, the most common places that you may experience symptoms include:
Your dermatologist (a doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the skin, hair, and nails) can easily detect contact dermatitis by reviewing your symptoms, recording a detailed medical history, and conducting a physical exam.
Your doctor may recommend a patch test to confirm the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis. A sticky patch coated with different allergens is placed on your skin. When the patch is removed after some time, your dermatologist will observe if the known allergens cause any allergic reactions. Sometimes, your doctor may recommend a biopsy to rule out other skin conditions, although it is rare.
Treatment for contact dermatitis is the same for allergic and irritant contact dermatitis. Options include:
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes an itchy rash when you come in contact with an allergen or an irritant. Your doctor can help you identify the allergen or irritant and how to avoid them and keep yourself safe from itchy, painful rashes. If you notice any skin rash after contacting substances like detergents, soaps, acids, or fragrances, contact your dermatologist for further evaluation and management.
Contact dermatitis is not usually contagious. However, if anyone comes in contact with you and is allergic to the same allergen or irritant, they can develop a skin rash, too. Every person's body reaction is unique.
Contact dermatitis can spread to other parts of your body, depending on what causes it. Allergic contact dermatitis can be easily spread. If you touch an allergen and other parts of your body, you may spread the skin rash to those parts. Contact your doctor immediately if you notice your rash spreading to other body parts.
It may take several days to weeks for the skin rash caused by contact dermatitis to go away with treatment. Symptoms like pain, itching, or a burning sensation may gradually reduce a couple of days after treatment, although you may still notice visible signs of a rash. Mild cases of dermatitis may go away without treatment if you avoid what caused or triggered the allergic reaction.
Complications of contact dermatitis include: