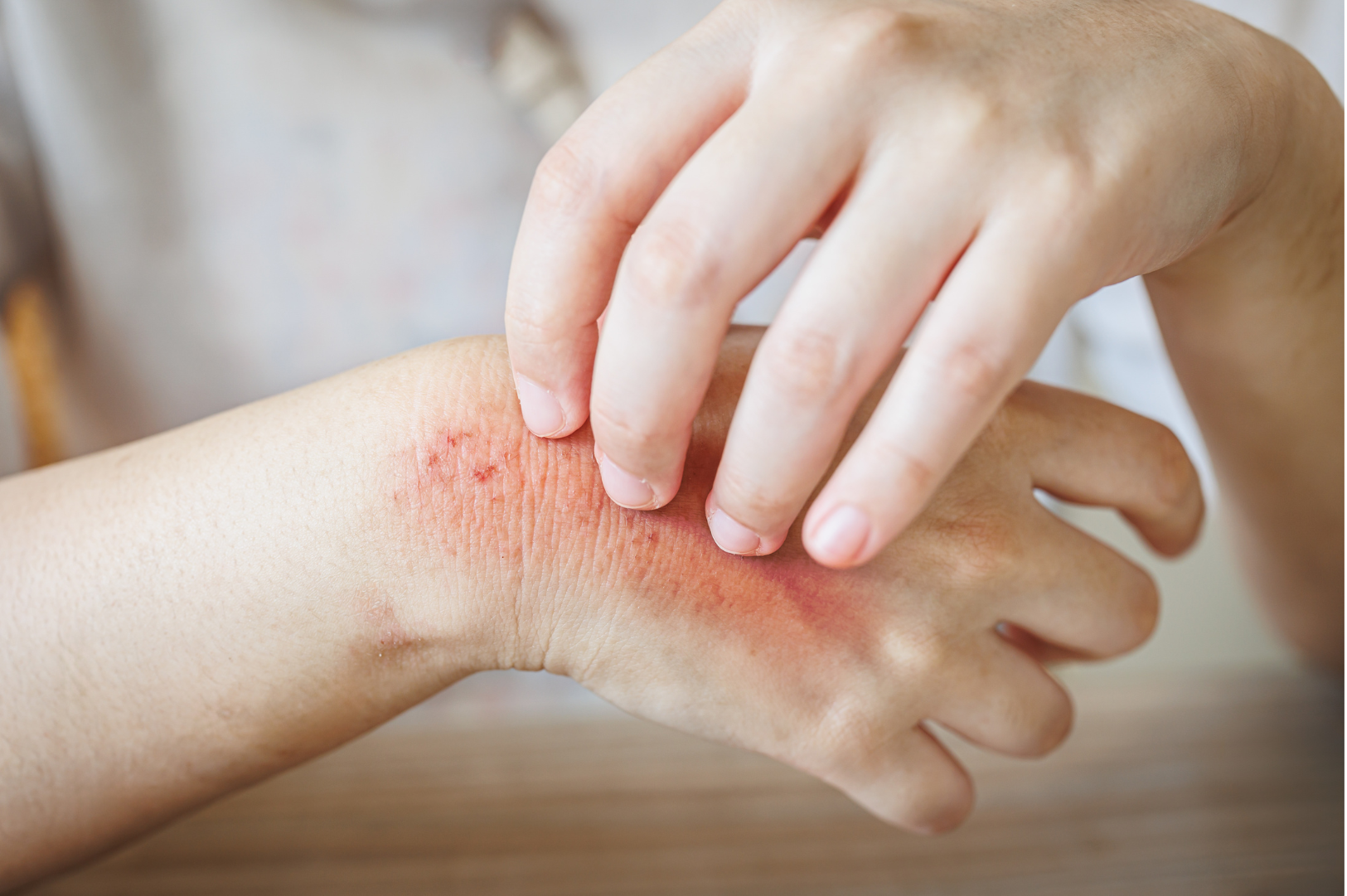
Infections are abnormal invasions and the growth of germs in your body that result in skin rashes, fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. They can infect your skin and other body parts like the lungs, liver, and brain. You can acquire a parasitic infection from contaminated water, food, or surfaces, bug bites, and eating undercooked food. Parasitic infections are often treated with the help of antiparasitic drugs prescribed by your dermatologist (a doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the skin, hair, and nails).
Read this informative blog below to learn more about parasitic infections, their types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Parasitic infections are conditions or illnesses caused by parasites living and reproducing in your body. Parasites are microorganisms that require a host cell to get the nutrients they need for survival.
Parasitic infections can affect your skin or other body parts, such as the internal organs, such as the lungs, liver, kidneys, or brain. Depending on the location, they can develop a series of symptoms.
Three main types of parasites cause infections in humans. These include:
The most common parasitic infections include:
You can get parasitic infections from the following:
Anyone can get parasitic infections; however, you are more prone to developing them due to certain risk factors. These include:
Symptoms of parasitic infections depend on the area of your body being infected.
Doctors or dermatologists can diagnose parasitic infections by detecting parasites in body fluids or tissues.
Your doctor might use the following samples for testing:
Other diagnostic tests may include:
Furthermore, your doctor may order imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to diagnose parasitic infections.
Your treatment plan will depend on your specific diagnosis. A combination of medications is usually effective for parasitic infections.
These include:
Other supportive care tips include:
There are several steps to take that can reduce your risk of contracting a parasitic infection:
Parasitic infections can affect millions of people globally. Some of you may show no symptoms of infection, while others can experience fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, skin rash, and so on. Untreated parasitic infections can even be life-threatening. Most doctors treat parasitic infections through appropriate medications. You can even take preventive steps to reduce your risk of developing parasitic infections, especially while traveling. If you notice any symptoms of parasitic infection, seek help from an experienced doctor or dermatologist for further evaluation.
1. When should you consider going to the emergency room if suffering from parasitic infection?
You must go to the emergency room if you experience any of the following symptoms:
2. Are parasites contagious?
The parasites are contagious and can easily spread to other people through exposure to an infected person's blood. For example, by blood transfusion or by sharing needles contaminated with blood.
3. What foods can help clear parasites from your digestive tract?
The following foods help clear parasites from your digestive tract:
4. Can parasites go away on their own?
Some parasites can go away independently, especially if you have a healthy immune system and lifestyle with a well-balanced diet and adequate hydration. However, some may require medical intervention.