Normal skin is usually colonized by bacterial flora that live as commensals on the surface or hair follicles. But, sometimes, bacterial overgrowth can cause skin diseases. A skin sore (a skin lesion or ulcer) is often a physical symptom of an underlying skin condition. Such physical symptoms can negatively impact your life due to pain or unaesthetic appearance. Impetigo is one such bacterial skin infection that is highly contagious. Commonly affecting children, impetigo with sores and blisters around the mouth and nose is a common sign. Though impetigo may resolve on its own, dermatologists (doctors specializing in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the skin, hair, and nails) suggest treating the condition with antibiotics to prevent complications.
If you are wondering what exactly happens when an impetigo infects a child, read on as we help you understand the condition better.
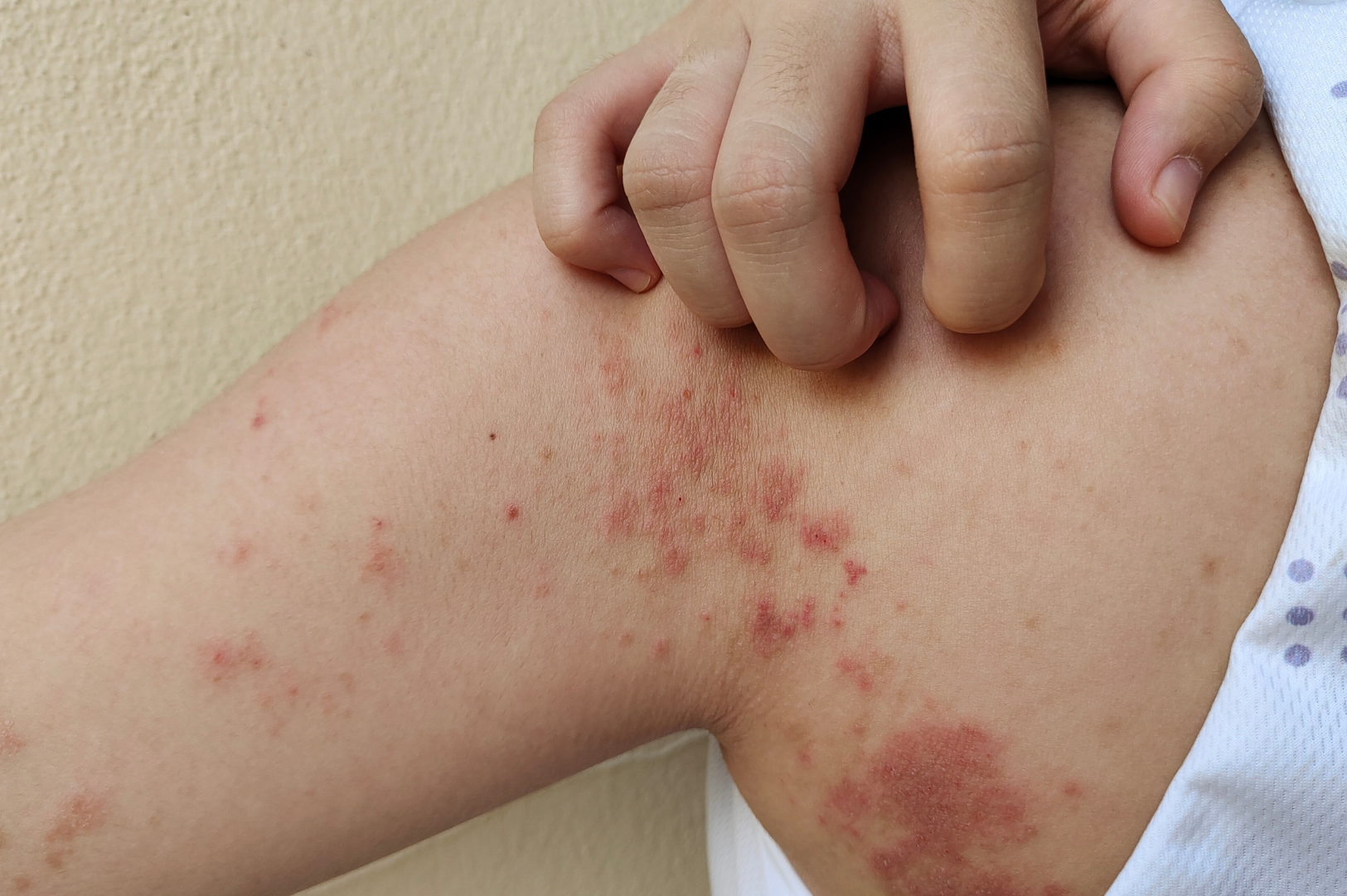
Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection that spreads easily. It commonly affects children, especially those 2 to 5 years old, though it can appear at any age. It causes itchy, painful skin sores that may heal and form crusts around the mouth and nose. It can also appear on your child's scalp, hairline, legs, and arms.
Bacterial invasion and overgrowth lead to impetigo, which happens when your child gets a cut, bite, or scratch. This skin condition occurs more often during summer. Impetigo can be confused with cold sores, but the blisters in cold sores are smaller and appear only around the mouth.
Impetigo sores and blisters can present differently based on the type and your skin tone. There are three main types of impetigo, namely:
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact. The condition can be contagious for several weeks without proper treatment until the rashes disappear or the scabs fall off. Other modes of spread from an infected person include:
Bacteria cause impetigo, usually the staphylococcus or streptococcus organisms. Several other factors can increase your likelihood of impetigo. These include:
The symptoms may vary based on the type of impetigo and appear within three days of bacterial invasion. These include:
Dermatologists can quickly diagnose impetigo through its appearance. However, your doctor may recommend a skin culture to study the type of bacteria causing the infection. This helps them determine and prescribe the right antibiotics to treat the condition.
Impetigo is usually treated with antibiotics that help eliminate bacterial infections. These include:
Home remedies can help manage your symptoms and aid in quick healing. However, consult your doctor before using them. Also, remember they should always be used in addition to antibiotic treatment, not as a replacement. Some effective home remedies include:
Though impetigo cannot be completely prevented, you or your child can follow the below tips to prevent their spread.
Impetigo is a common bacterial infection of the skin that commonly affects children. Though the condition is not dangerous, it is highly contagious and spreads easily when in contact with an infected person. Seek medical care when you notice any rash or sore near your mouth or nose. Doctors can help clear impetigo through antibiotics. Good hygiene and caring for your impetigo blisters can help prevent the spread of infection to others and help you heal faster.
If you suspect your loved one has impetigo, consult a dermatologist immediately for further evaluation.