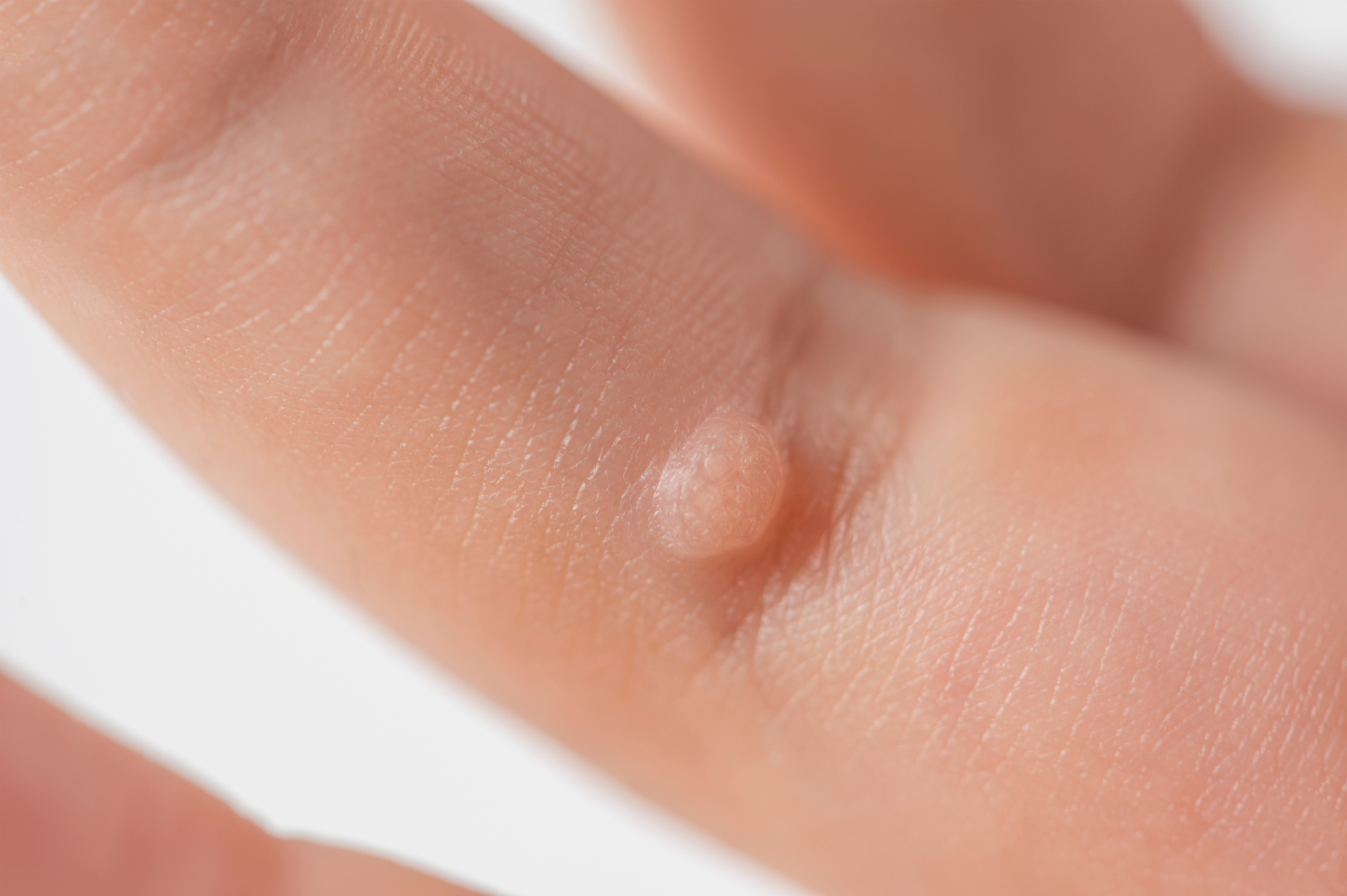
Warts are small, benign (noncancerous) bumps that form anywhere in your body that are extremely painful. These bumps are caused by HPV entering your body through cuts or scraps and can easily spread through physical contact. There are several types of HPV warts, but this article will explore in detail about genital warts. These are types of warts that appear in the pubic area, on your genitals, in or around the anus, and in the vagina. Genital warts are a type of sexually transmitted infection that is highly contagious. Though HPV cannot be cured, different treatment options may be recommended to remove the bumps or skin overgrowths.
To learn more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of genital warts, keep reading!
Genital warts are a type of sexually transmitted infection that causes small growths like bumps to form in and around your genitals. These warts are caused by certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). Genital warts affect the moist tissue of your genital areas, and the bumps may resemble a cauliflower. These are, however, too tiny to be seen through the naked eye.
Genital warts can affect all genders; however, male teenagers or young adults are more prone. These bumps are seen developing near your:
Yes, HPV and genital warts are both contagious and can quickly spread to others. There is no definite cure for HPV, and once you have the virus, you are always infectious and prone to spread it to others. Even if you do not experience symptoms or have removed the warts, you can still be contagious and spread the virus to others. They commonly spread through skin-to-skin contact through sexual contact.
Genital warts are often caused by strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). Genital warts spread through:
Certain risk factors can increase your susceptibility to develop genital warts. These include:
You may experience the following symptoms of genital warts:
Your doctor can diagnose genital warts by their cauliflower-like bumps in your genital areas. However, internal warts are more challenging to diagnose. Doctors may recommend the following to confirm genital warts:
Genital warts cannot be completely cured. Yet treatment may help manage their growth and reduce your chances of spreading the infection to others, as an active outbreak spreads more easily. There are several treatment options to remove genital warts, and you may need a combination of those options. Remember, during your treatment, you must avoid any kind of sexual contact.
Treatment options include:
You can take the following steps to protect yourself from getting or spreading HPV, genital warts, and other STIs:
Genital warts are the most common type of sexually transmitted infections caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). Thousands of people may suffer from this condition with or without having symptoms. Genital warts are highly contagious and spread through sexual contact. There is no cure for HPV or genital warts. Once you have them, you are always infected. If you notice any bumps near your genital areas, consult your doctor for further evaluation and management.
1. Can I get genital warts more than once?
Yes. You can get genital warts more than once since there is no cure for HPV; even after the removal of the warts, you are still infected and may get genital warts again and again.
2. How common are genital warts?
It is estimated that around 3 to 4 lakh people may be infected with HPV yearly. About one in 100 sexually active teenagers and adults may have genital warts at any given time.
3. How long do genital warts last?
Genital warts and HPV are lifelong conditions. Even after treating the warts and removing them, they may come back.
4. How soon do genital warts appear after infection?
You may develop genital warts within weeks of sexual contact with an infected person. However, warts can also take months or even years to appear. You can also have the virus and not show any symptoms, which can be dangerous since you may unknowingly infect others with the virus.