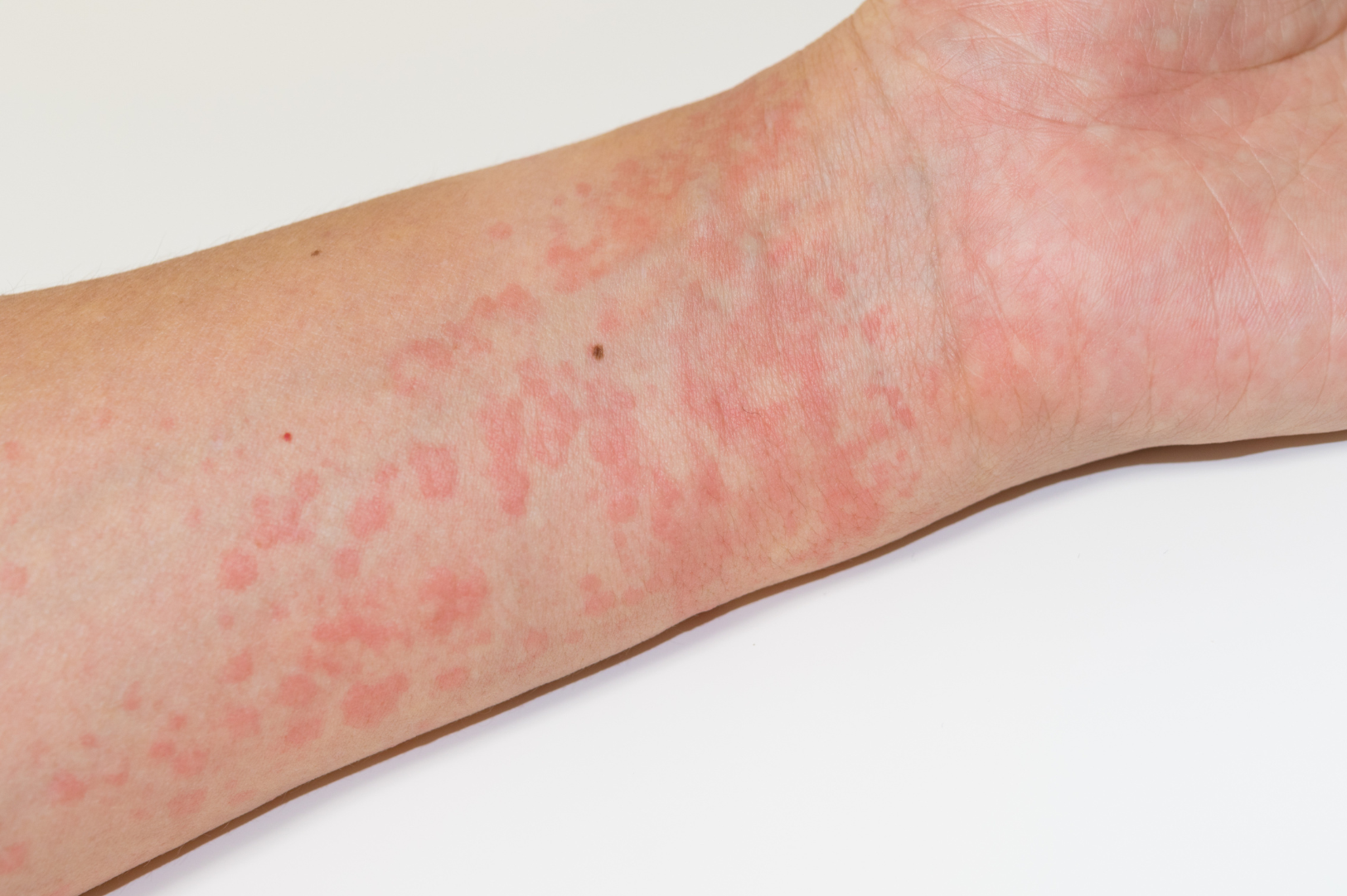
Are you experiencing sudden red, raised, itchy, tiny welts or bumps in different parts of your body? You might have eaten or touched something that has caused you an allergic reaction. These bumps may sometimes be irritating, causing a burning or stinging sensation. You may also experience a slow onset of these itchy rashes or bumps. These could be “Hives.” Whatever the reason, hives can be very uncomfortable, negatively impacting your sleep and quality of life.
Hives, also known as urticaria, can go away quickly (acute hives) or may last longer (chronic hives). To learn more about hives, their types, causes, symptoms, diagnoses, and management, scroll down!
Hives, medically known as urticaria, are a type of skin condition characterized by red, raised welts (bumps) on the skin. They are often a swelling on the surface of the skin caused by an allergic reaction.
Allergic reactions occur when your immune system comes in contact with an allergen (proteins that are usually harmless to many but may cause an allergic reaction in sensitive people). Hives appear as small as a fingertip or as big as a dinner plate. Sometimes, the bumps may join together to form larger areas called plaques.
There are several types of Hives, namely:
Your skin consists of immune cells called mast cells. When a foreign invader or allergen enters your body, these cells may get activated, releasing chemicals called histamine. Tiny blood vessels called capillaries may leak fluid and begin to accumulate in the skin, causing inflammation and a rash. As fluid continues to accumulate under the skin, small bumps form.
Causes of hives depend on the type of condition, including:
Medications that cause hives:
Certain antibiotics
NSAIDS (Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs) like aspirin
Antihypertensives
Examples of viral infection:
Hepatitis
Colds
Other infections
Autoimmune Conditions like lupus, diabetes, celiac disease
Hypothyroidism
Intestinal parasites
Physical factors other than allergens can also be responsible for triggering hives. These include:
Depending on the type of condition, you may show different signs and symptoms of hives. These include:
Chronic hives may be similar to acute hives; however, there could be certain differences. Chronic hives:
Your dermatologist (a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the skin, hair, and nails) can easily diagnose hives by examining your skin.
However, your doctor may recommend allergy tests to determine the cause. These include:
The best approach to treating hives depends on the cause and type of the condition.
These types of hives usually disappear on their own within a few days. However, treatment may include:
Severe forms of acute hives may require a prescription of epinephrine in the form of an auto-injector.
This hive may not resolve on its own and may require medical intervention. Antihistamines should be taken regularly until the symptoms resolve.
Several at-home tips can help reduce hives symptoms. These include:
You can effectively prevent hives by adopting several preventive measures, such as:
Hives, commonly known as urticaria, are a type of skin rash characterized by itchy, irritating red welts or bumps on different parts of the body. They may result from an allergy, underlying health condition, or other triggers. Hives may either be short-lived (acute) or long-lasting ( chronic) and often require treatment using a suitable antihistamine.
If you notice any allergens triggering an allergic reaction and causing hives, it is better to avoid them. If hives are affecting your quality of life, consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment.