An abnormal invasion and growth of germs in your body is known as infection. The germs may be bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms. This informative blog will highlight fungal infections caused by fungi or yeast. These infections usually affect your skin, hair, nails, or mucous membranes. However, they can also affect other organs like your lungs, kidneys, liver, etc. Anyone can get fungal infections, but people with other health conditions like diabetes, HIV, or cancer are more prone to develop the infection. Most fungal infections are not serious or life-threatening and can be easily treated through antifungal medications.
Keep scrolling to learn more about fungal infections, their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Fungal infections are also known as mycosis. These are diseases caused by a fungus (yeast or mold) that are most commonly seen developing in the skin, hair, and nails. However, they can also cause infections in the mouth, throat, lungs, liver, urinary tract, and many other parts of the body.
Fungi are living things that live naturally in your body but can outgrow under certain circumstances. They can easily move around and spread by passing out or sending spores (reproductive parts of fungi) into the air or environment.
Several types of fungal infections have been noted based on the areas in which they affect. These can be classified into:
Tinea pedis or athlete's feet (affecting the feet)
Jock itch (groins and inner thigh)
Tinea Capitis (scalp)
Tinea manuum (hands)
Tinea barbae ( facial hair)
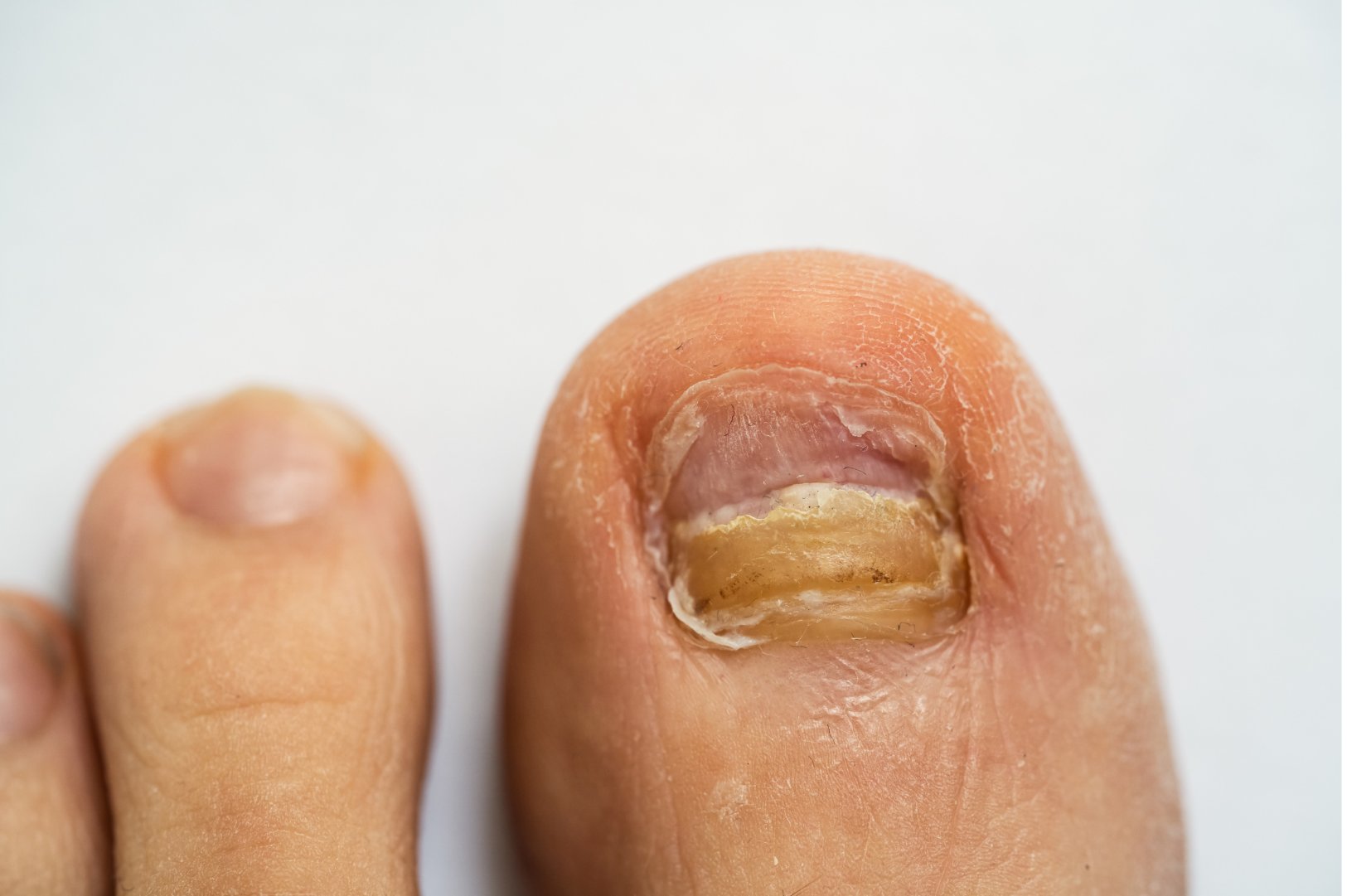
Onychomycosis
Affect your fingernails and toenails
Candidiasis
Affects the skin and mucous membranes
Tinea versicolor
The yeast Malassezia affects the skin
Sporotrichosis
Chromoblastomycosis
Eumycetoma
Examples include:
Histoplasmosis
Valley fever
Blastomycosis
Aspergillosis
Candidal urinary tract infection
Invasive candidiasis
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Mucormycosis
Cryptococcosis
Yeasts, molds, and other types of fungi cause fungal infections. Some common fungi-causing diseases include the following:
The fungi can spread easily through the following ways:
Symptoms of fungal infections depend on the type of infection and the area of your body affected.
Your dermatologist can identify a fungal infection based on the signs and symptoms. Your doctor may recommend a culture test using the following samples:
Furthermore, you may be advised to get the following imaging tests for deep fungal infections affecting the internal organs:
Your doctor may treat fungal infections with the help of antifungal medications. This depends on the type of condition and the location where it develops.
To treat fungal disease, your doctor may prescribe antifungal drugs in the form of:
Practicing good personal hygiene and protecting yourself from the environmental fungi. Follow the below-mentioned tips to prevent fungal infections:
Fungal infections are common but can be uncomfortable or even painful. Depending on the type of infection and the areas of your body affected, it may take days, weeks, or months to treat them. Seek help from a dermatologist who can diagnose fungal infections and recommend an appropriate treatment plan that works best for you.
1. Are fungal infections contagious?
Superficial fungal infections like ringworm are highly contagious and may spread from person to person through direct contact. However, deep fungal infections affecting organs like the lungs and brain are not contagious.
2. How long does a fungal infection take to heal?
It may take a few days for the symptoms of a fungal infection to go away. Redness and itchiness may go away after a few days of treatment. Skin discoloration and scaliness may take up to a few weeks to completely heal.
3. Will fungal infection go on its own?
Fungal infection requires treatment and usually does not go away on its own. Leaving the infection untreated may result in the spreading or worsening of the symptoms.