Have you noticed any swelling, lump, or bump on your skin? Is the lump freely movable? Worry not, this could be a simple cyst that is usually a sac filled with fluids. You may confuse this with other skin growths like lipoma, but consult a health professional to clear your doubt. Cysts are common entities that are usually benign (non-cancerous), harmless, and painless. These may appear superficially on the skin surface or present deeper inside your body. Several causes like tumors, injury impact, and infections can lead to the development of cysts. Often, cysts do not cause any symptoms, but pain and discomfort may follow if they compress an underlying tissue, organ, nerve, or blood vessel. Seek timely medical care for an in-depth evaluation of your skin growth to be sure it isn't dangerous.
Keep reading to know everything about a cyst, from its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and home remedies.
Cysts are sac-like structures typically containing a fluid, semi-solid, or gaseous material, like a blister. These dome-shaped capsules can occur almost anywhere in your body, like the face, hands, neck, back, and arms, and within internal organs like the brain, liver, kidneys, etc. Most cysts are benign (non-cancerous), but a few may contain malignant (cancerous) cells. Cysts are harmless and painless entities unless they get infected or turn cancerous.
There are several types of cysts based on their location. These include:
Acne Cyst or Cystic Acne
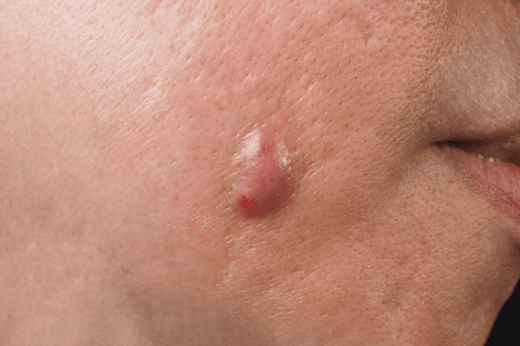
Epidermoid Cyst
Sebaceous Cyst
Pilonidal Cyst
Mucous Cyst
Ingrown Hair Cyst (Folliculitis)
Pilar Cyst
These are located deep in your body, usually affecting internal tissues, muscles, ligaments, and organs. These include:
The following are some of the major and common causes of a cyst:
Most often, a cyst may not cause any symptoms except for a noticeable lump. This is especially true in skin cysts, which may cause a fluid-filled sac that may or may not be painful. Other signs and symptoms include:
Deeper cysts developing within the internal organs usually have no symptoms. However, if they enlarge in size, compressing any organs, nerves, or blood vessels, then pain or other symptoms related to those organs may develop.
Your doctor can diagnose superficial cysts easily due to a prominent swelling or lump. A detailed medical and family history will be recorded to evaluate any genetic predisposition or history of previous injuries. A physical examination can help assess whether the cyst is palpable and tender on touch.
Your doctor may advise imaging tests like ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans for deeper cysts. Furthermore, biopsy tests can help determine the nature of the fluid within the cyst and the presence of any malignant cells.
Treating a cyst usually depends on the lump's type, location, and size. Most often, cysts do not require any treatment if they are benign without any symptoms. However, larger cysts may require treatment mainly for cosmetic purposes or symptoms due to compression of the underlying nerves, blood vessels, or organs.
Treatment options include:
Several home remedies may help shrink the cyst, but consult your doctor before trying them. Also, avoid pricking or popping the cyst since this may worsen the symptoms and spread the infection to other parts.
Home remedies include:
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop anywhere in your body. They are relatively common, and there are many different types based on the cause and location of the swelling. Several reasons, like injury, infections, and tumors, can cause a cyst, with a genetic predisposition increasing your likelihood of developing one. They are usually benign but can become cancerous sometimes.
If you notice any lump or skin changes, it is best to contact your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. Doctors may recommend steroid injections, cyst drainage, surgical removal, or laser therapy to get rid of aesthetically unappealing, painful, and infected cysts.