- This information was developed by GMR Web Team.
- This information is intended only to provide general guidance. It does not provide definitive medical advice.
- It is important that you consult your doctor about your specific condition.
Bowen's Disease
Bowen's disease is an early form of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which is a type of common skin cancer. It is accompanied by slow-growing cancerous cell changes that cause scaly patches on the skin. However, it is important to note that this skin cancer is confined only to the epidermis, the superficial layer of the skin. The skin lesions may mimic other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis; thus, it is important to get them evaluated by a skilled and qualified dermatologist (a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the skin, hair, and nails) for an accurate diagnosis. Since it is a type of skin cancer, it is essential to get yourself treated at the earliest.
Read on to learn about the causes and symptoms of Bowen's disease, plus how it's diagnosed and treated.
What is Bowen's Disease?
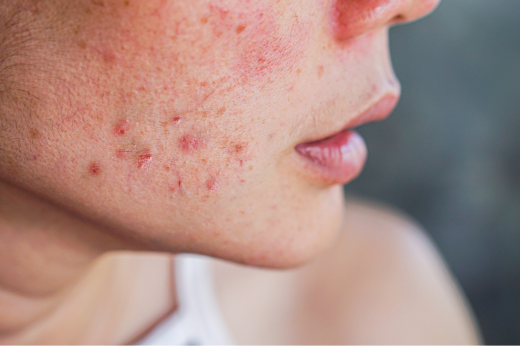
Bowen's disease, sometimes called squamous cell carcinoma in situ, is a slow-growing skin cancer that appears only within the epidermis. The cell changes occur gradually and do not cause much trouble to most people. It is a non-contagious skin condition that may mimic psoriasis and eczema. If not treated, Bowen's disease can occasionally develop into squamous cell carcinoma (about 5 in every 100 people having Bowen's disease).
Bowen's disease often develops as red scaly patches in areas exposed to the sun. Women over the age of 40 are more likely to develop this type of skin cancer.
What Causes Bowen's Disease?
The exact and specific cause of Bowen's disease is unknown. However, several research studies have found certain factors associated with it.
Chronic UV (Ultraviolet) Radiation Exposure
- Prolonged exposure to UV radiation causes red, scaly patches on your skin.
- The sources of UV radiation include:
- Tanning beds
- Sunlight
- Mercury vapor lighting (as seen in stadiums)
- Halogen and fluorescent lights
Compromised Immune System
- A mutation of a specific gene, such as p53, can lead to various forms of skin cancer.
- A weak immunity can increase the p53 gene mutation.
- Causes of weak immunity include:
- Having a genetic disorder
- Receiving radiation therapy
- Taking immunosuppressant drugs
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
- HPV virus can lead to scaly red patches on your skin.
Chronic Arsenic Exposure
- Arsenic is a tasteless and odorless metal that is toxic to humans.
- Chronic exposure to arsenic (over ten years) can cause Bowen's disease.
- Modes for arsenic exposure include:
- Drinking water containing arsenic
- Smoking
- Tobacco products
- Exposure to landfills
- Living near industrialized areas
Who Gets Bowen's Disease?
People with certain risk factors can have increased susceptibility to develop Bowen's disease. These include:
- Being a female
- Age above 40 years
- Having a light skin tone
- Having a photosensitive skin
- Having a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer
What Are the Signs of Bowen's Disease?
Bowen's disease usually causes a single lesion for most people, while 10 to 20% of them develop multiple lesions. The skin lesions commonly develop on the face, head, neck, arms, chest, and legs. However, they can even be seen in areas such as the lips, oral cavity, and the genital area.
The signs of Bowen's disease include:
- Red scaly patches that persist for months to years
- The patches may be slightly raised or flat and may be in the form of nodules
- You may have a single or multiple patches on your skin
- The patches have irregular edges and borders
- The patches grow and enlarge gradually
- The patches may be tender on touch
- They may itch and bleed easily
- When infected, you may notice pus oozing out of the patches, which eventually leads to crusting
How do Doctors Diagnose Bowen's Disease?
Your doctor may refer you to a skilled dermatologist to confirm the presence of Bowen's disease. The dermatologist may clinically examine your skin to evaluate the patches. Furthermore, they may order a biopsy, in which a small tissue sample is extracted and studied under a microscope.
How is Bowen's Disease Treated?
The best treatment for Bowen's disease depends on the size of the skin lesion, their number, thickness, location, and your overall health status.
Treatment options include:
Surgical Removal
- It is useful for smaller lesions and is a common method of treating Bowen's disease.
- It is performed under local anesthesia to numb the area and cut out the lesion along with a thin margin of the surrounding healthy skin.
- It is the most effective method but leaves behind a scar.
Topical Chemotherapy
- A medicated cream is applied directly on the skin lesion to destroy the cancer cells.
- It may be used in combination with other treatment options.
Cryosurgery
- Also known as cryotherapy, this option uses cold temperatures, such as liquid nitrogen or argon gas, to destroy cancer cells.
- This is usually recommended if you have a single skin lesion.
Curettage with Electrocautery
- Curettage involves scraping the skin lesion using a special instrument called a curette.
- This is followed by burning the lesion with an electric current, called cauterization.
Radiotherapy
- This method uses high doses of radiation to destroy the lesion.
- Several types of radiation therapy include:
- External beam radiotherapy
- A radioactive skin patch
- Grenz rays
Topical Photodynamic Therapy
- A light-sensitizing agent is applied to the skin lesion for 3 hours.
- Then, a special light is directed to the area concerned to destroy the lesion.
Can You Prevent Bowen's Disease?
Although you cannot completely prevent Bowen's disease, you can decrease your risk of developing the condition with the following preventive tips:
- Refrain from using a tanning bed
- Avoid working outdoors under direct sunlight
- Wear protective clothing when outdoors
- Wear sunscreen with a good SPF and reapply it frequently.
Final Thought
Bowen's disease is a cancerous condition, a slow-growing form of squamous cell carcinoma. It involves scaly red patches that turn into skin cancer over time. The most common cause is prolonged sun exposure, but it may also be caused due to HPV infection, arsenic exposure, and a compromised immune system. Consult your dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and management if you notice any skin changes. Treatment for Bowen's disease is based on several factors and may involve options such as surgical removal, radiotherapy, topical chemotherapy, curettage, cauterization, and cryotherapy.
When treated early, Bowen's disease has a high recovery rate.
