Skin cancer is a common type of cancer that affects your body and develops due to abnormal growth of skin cells, namely the melanocytes, keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel's cells. This type of cancer commonly develops in sun-exposed areas. However, it can also occur in other areas of your body. There are several skin cancers, but the one discussed in this article is "Basal cell carcinoma." This type of skin cancer causes a lump, bump, or lesion on the superficial layer of the skin known as the epidermis. It commonly occurs more in men than women over the age of 50 years.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer overall and the most common type of skin cancer. Read on to learn about basal cell carcinoma and be well-informed about seeking medical help at the right time.
Basal cells are microscopic cells in the outer layer of your skin (epidermis). These cells make new skin cells by dividing and multiplying themselves. When basal cells create new cells, the older skin cells push to the surface of your epidermis, where they die and leave your body.
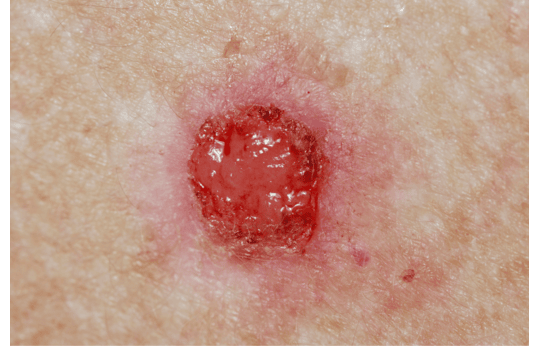
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a type of skin cancer that forms on the basal cells in your skin. It looks like a small, shiny bump or scaly, flat patch on your skin that gradually grows over time. It initially begins on your nose or other parts of your face, but you can get bumps or patches on any of your body parts, including your trunk, legs, and arms.
The cancer is unlikely to spread to other body parts but can move nearby into bone or other tissues under your skin. Basal cell carcinoma grows very slowly and often doesn't appear for many years.
There are four main types of basal cell carcinoma, including:
Research studies believe abnormal changes in your DNA cause basal cell carcinoma. These DNA mutations commonly occur due to chronic sun exposure from sunlight or tanning beds.
Abnormal DNA and gene mutation cause the basal cells to produce too many cells, which causes lumps or lesions to form in the outer layer of your skin (epidermis). Furthermore, a rare form of inherited condition called nevus syndrome can cause BCC in childhood.
Risk factors for BCC include:
Basal cell carcinoma commonly appears on areas of your body exposed to the sun for a prolonged period. Your face, scalp, nose, eyelids, legs, ears, and arms are common areas where you can develop BCC lumps.
The symptoms of BCC include:
If you notice any lump or scar, consult a doctor for further evaluation. Your doctor may diagnose BCC through a physical exam and diagnostic tests. The physical examination helps determine the type of BCC, its extent, and how fast it has been growing.
Additionally, your doctor may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
Treatment for BCC depends on the type and extent of the cancer. Treatment options include:
Although all cases of BCC cannot be prevented, you can certainly adopt a few steps to reduce your risk. These include:
Finding a cancerous lump in your body can be scary and daunting. Basal cell carcinoma is a common type of skin cancer that develops due to the overproduction of skin cells by the basal cells due to an abnormal gene and DNA mutation. Consult your dermatologist immediately if you notice any lumps or scars on your face, eyelids, nose, scalp, trunk, arms, or legs for further evaluation. Early detection and prompt treatment for BCC pave the way for a positive prognosis and enable you to improve your quality of life.